
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4488
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF
SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING FOREHAND AND BACKHAND
DRIVE
Farwa Babar
1
, M. Farhan Tabassum
1*
, Sumera Sattar
2
, Noor ul An Babar
1
, Saadia
Hassan
1
, Saman
2
, Rabia Karim
1
1
Department of Sports Sciences & Physical Education, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences,
University of Lahore. Lahore, 54000, Pakistan.
2
Health & Physical Education department, Lahore College for Women University Lahore.
Lahore, 54000, Pakistan.
Farwa Babar
, M. Farhan Tabassum
, Sumera Sattar
, Noor ul An Babar
, Saadia
Hassan
, Saman
, Rabia Karim
, Analysis Of Table Tennis Skills: An Assessment Of
Shadow Practice In Learning Forehand And Backhand Drive , Palarch’s Journal Of
Archaeology Of Egypt/Egyptology 18(8), 4488-4502. ISSN 1567-214x.
Keywords: Table Tennis, Drive-skills, Sports Sciences, Shadow Practice, Physical
Education, Coaching.
ABSTRACT: The aim of the study was to examine the performance of university female-
athletes particularly using shadow practice in learning the standardized table tennis forehand and
backhand-drive in a restricted practice time as physical education lesson or sports period in
feedback of the problem on accordingly develop training design that will assist learning of
Table-Tennis. Twenty student-athletes from two different universities were selected and divided
into two groups. The five-participants of experimental group were asked to do forehand-drive
shadow training in mix with multiple-ball training and five participants of experimental group
performed backhand-drive shadow practice with combination of multiple-ball training. The same
procedure used five by five (forehand and backhand-drive) participants of Control group
performed one ball for every pair of athletes in blend with multiple-ball training. The two groups
were analyzed in three testing stages. The test was conducted on one subject at a time. Each
subject was instructed to hit the fed balls to the designated target area at the opposite court
(crosscourt). The number of balls that hit the specified target area was counted and became the
subject’s score. First, the pre-test, which was conducted after being given instructions on how the
forehand as well as backhand drive is done. Second, a post-test was done after the four weeks of

ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4489
continuous training. And finally, the retention test was given after three calendar days after the
post-test. There was a significant improvement of the mean and standard deviation scores from
the pre-test to post-test in both the Experimental and Control Groups. The Experimental Group
(Forehand SP) went from a mean score of 18.80 ± 1.924 to 39.20 ± 1.140 and Experimental
Group (Backhand SP) mean score of 18.60 ± 1.140 to 39.60 ± 1.140 while the Control Group
(Forehand single-ball) went from 18.60 ± 2.302 to 38 ± 1.581 and Control Group (Backhand
single-ball) mean score of 18.40 ± 2.074 to 38 ± 1.81. Both groups were able to retain their mean
scores in the retention test (FSP) 39.40 ± 1.140 and (BSP) 39.80 for the Experimental Group and
(F-Single-ball) 35.80 ± 1.304 and (B-single-ball) 36.20 ± 1.304 for the Control Group). Although
the mean score of the Experimental Group was higher, there were no significant differences in
the scores from the Post to the Retention tests of both groups (p > 0.05). The study revealed that
both the Experimental Group and Control Group had a significant change in their scores in the
post-test phase of testing. Both Experimental Group and Control Group were able to retain their
scores.However, the Experimental-Group was only able to maintain their scores in RT.
INTRODUCTION
Besides being a pleasant method to go through an evening with your loved ones, table tennis
additionally offers shockingly extraordinary medical advantages. Like most games, table tennis
offers extraordinary mentally-physically stimulation, high-impact exercise, and social
association. In contrast to numerous games, nonetheless, the inclusive danger for injury with
table tennis is very low. At the point when it is played seriously, it is an incredible method to get
fit and burn-out calories. There are a large number of sports everywhere in the world which root
injuries each year to numerous individuals however while playing table tennis you can profit all
the medical advantages without having a more serious danger of being injured. Besides, there are
not many indoor games in which physical exercise is included. Table Tennis is one of those
indoor games which includes dynamic interest genuinely. One of the advantages of playing table
tennis is that it gives an exercise to your brain that not just retains you physically, moreover
intellectually fit. Indeed, Table tennis assist you enhancing your speed, strength, and agility.
"It is logically demonstrated that if you get the chance to play table tennis for only 10 minutes
every day, it helps action in the prefrontal cortex and cerebellum."
Shadow training, sometime called shadow practice, is depicted as a repeated activity mirroring
the particular expertise utilized in the specific game. SP is a practical method applied to gain
proficiency with a best possible structure required at the right implementation of an expertise by
repeated movement. In TT, shadow training is the point at where an athlete rehearses his hitting
method while lacking of ball. It resembles a type of pretending wherein the hit is rehearsed
similarly as it would in an ordinary play. The nonappearance of the ball permits the athlete to
focus on attaining his practice right, and what the right strategy feels like. SP could be a
significant practice instrument whenever finished with accurate thoughtfulness regarding
structure.
The fundamental strokes utilized in TT accomplished utilizing either the forehand-hit or
otherwise the backhand-drive, top-spin, smash, push and flick. In table tennis, as in many games,
it's vital to get the specialized mechanics right. These fundamental strokes are the establishments
that can be based upon as a player improves. There are four fundamental table tennis strokes and
generally endeavor to have all players ace these before proceeding onward to progressively

ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4490
complex exercises. This investigation focusses on basically usefulness of shadow-practice on the
forehand and backhand hit-drive while it is a significant ability to acquire. The forehand drive is
the essential and first technique on the table that every single beginner player must learn so as to
learn table tennis sports. New player ought to become familiar with this procedure cautiously in
light of the fact that it's vital to gain proficiency with the right weight move. It is likewise
encouraging you to feel the ball figure out and acquire how to affectively create spin in the ball.
As general rule, before preparing the forehand topspin, you should exercise the forehand drive
procedure first. Furthermore, in table tennis a good backhand technique is also very important in
a game because a well-developed backhand adjusts a decent forehand in securing the table
during play. Focuses could be certainly achieved whether the ball is designated to the backhand
table side of a rival with a frail backhand drive expertise. Contrastingly, a dominant strike from
the backhand side is the least an opponent can anticipate. The BD is a helpful method in TT. It
could supplement the forehand-side by making backhand stroke extra prevailing and might
equally reimburse for athletes those with slower footwork. Despite the fact that the forehand-
drive is a lot complex ability as compared to the backhand-drive, though we can't limit the
advantages of possess an incredible backhand drive. It tends to be utilized to operate for further
impressive strike or, it possibly be simply the genuine attack. The backhand-drive is valuable in
competition play and likely to improve a TT athlete's strike stockpile.
(Mehmet Fatih YÜKSEL, 2017) did a research to see the impact of shadow badminton practice
about the motoric characteristics of badminton athletes. The reason of research was to explored
the effects of twelve-week shadow badminton practice about physical presentation boundaries of
8-10 age category of teen-agers. Furthermore, the point was to add up to assurance of specific
application recurrence and length of badminton practice of amateur’s level players of badminton
game by looking at teaching method of shadow badminton as well as traditional badminton. The
finding of the research was determined a development in physical-performance parameters of
participants of both training classes.
Multi-ball preparing is a powerful technique for table tennis practice session, which assumes a
significant job in improving athlete’s athletic abilities. In view of the creator's instructing
experience for a several years, this paper utilizes documentation, test, scientific measurements,
master interviews and other exploration strategies to record the bat recurrence of multi-ball
practice and single ball practice in College Table Tennis class with a similar practice content and
a similar unit of time. Also, record pulse and regaining pulse ratio and in practicing. At last,
make an evaluation and exploration in the subsequent information to measure and impact of the
practicing. (Wei Zheng, 2016).
TT is one of the most famous sports on the planet. As indicated in an article by the ISF, the
number of inhabitants in TT members has got more than three-hundred million around the world.
Playing TT is viewed as professional wellbeing brandishing side interest, which is commonly
acknowledged by an ever-increasing number of individuals who participate in bodily action
(Elzbieta Biernat, 2018). For example, a sane development, the qualities of TT play, include
difficult longitudinal developments of the physique which incorporate, increasing speed,
slowing, bearing variation, moving rapidly and parity completely assist athletes with creating
ideal hit creation (Olivier Girard, 2009). TT trainers watched the significance of molding and
been practical in assisting TT athletes accomplish a superior serious form. Towards effective in
the game, TT athletes generally approached to accomplish great power practice in the pre-season
equally a major aspect of their biological planning.
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4491
The study by (Florendo Fernando, 2007) on the usefulness of shadow practice and training
structured conducted previously. The examination was led because of the issue on the most
proficient method to build up a training construction that will advance knowledge in table tennis
bodily instruction lessons even with the constrained period and lacking practice area which is a
typical installation in Philippine’s setting. The twelve school students were chosen in the study
and considerer all were totally beginner and who ever held a racket were exclude from the study.
The result of the study was the effect of shadow-training is more prominent.
As far as anyone is concerned, this is the main examination that has given proof identified with
the connection between powerful equilibrium and multi-ball practice in pre-season TT game.
Reason for this examination was to evaluate the impacts of multi-ball practice on unique stance
mechanism utilizing the S-E-B-T through TT multi-ball practice. In view of the discoveries of
the examination, the outcomes and investigation could help mentors to all make their training
session more effective during preseason training. As anticipated, the finding of the investigation
demonstrated that the critical decline in vigorous equilibrium for the most part happened in stage
II, however the female members began to decay sooner than their male counterpart. In addition,
while postural mechanism began to diminish altogether, stretch X of COP movement appeared to
build further than saw at the warmup complete. The stretch Y of COP movement indicated huge
decreases when similar stages were associated. (Yaodong Gu, 2019)
The examination by Sinah Goode explored the generalizability of aftereffects of relevant
intervention impacts by stretching out past lab exploration to an arena situation. Female
participants (N = 30) mastered 3 badminton different serves whichever a blocked (down
impedance), sequential (blended interference), or arbitrary (high interference) training schedules.
The participants rehearsed the serves 3/7 days for 3 weeks. (Sinah Goode, 1986) A typical finish
of mechanical learning research focuses on the thinkable presentation of the information to an
instructive setting e.g., (John B Shea, 1979). Generalizability is to be sure one of the objectives
of science, yet not very many investigations have affirmed that tentatively devised outcomes are
consistent in a "genuine plant" situation (Whiting, 1982).
The investigation by Hebert inspected the impacts of training plan controls executed in an
instructive situation effect on performance as well as mastering of low-and high-gifted
understudies.
A hypothetical worldview used to examine instructing and learning is the mediational forms
viewpoint. Inside this system, students are seen as dynamic data processors whose intellect and
manners define the sort and measure of discovering that to what extent they have learn that
happens (Jacqueline M. Edwards, 1986) . This view holds that the essential part of the educator
is to make a situation helpful for learning. Moreover, it causes to notice the need to consider
understudy attributes while deciding the viability of instructional factors. (Edward P Hebert,
1996)
The study examined the effectiveness of shadow training in learning TT fore-hand and back-
hand counter-drive. It ought to be noticed that the forehand drive requires a more extended scope
of muscle development when contrasted with the backhand. The primary angle of the arm is
stretched out and weight moved to the peddle arm. In performing the forehand drive, the forearm
swings synchronous to the weight transferal to the next leg while bending the abdomen. A
forehand stroke is basically striking the ball with your hand's best expected angle. For example, a
right-hand would strike the ball through the right part of his body-side, while a left-hand would

ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4492
strike through the left side. Performing a forehand drive or push can be separated into four
segments – your position, the backswing, strike and the completion. Once mastered, the forehand
drive would convert one of your most utilized table tennis strokes. It frames the reason for
further developed strokes, for example, the blocking, the looping and the counter spinning, hence
it's surely significant to build up a solid and reliable stroke.
In the backhand counter-drive, the primary stance of the arm is flexed at the forearm and
balanced is centered. The ability is performed by expanding the arm while at the same time
doing a minor weight move from the help leg to the prevailing leg with practically zero abdomen
motion. In this way, the execution of the backhand counter-drive is less complex than that of the
forehand drive. A backhand stroke includes turning your arm marginally over your body to strike
the ball. Similar to forehand, the backhand could likewise be separated into four segments – your
position, the backswing, the strike and the completion. It is a significant volley that permits you
to control rallies, return rivals shots and step in proceeding attack mode yourself. In the event
when you neglect to master the backhand drive you will discover later on and find a lot harder
when you attempt to block with your backhand or play a more forceful topspin shot.
METHODS
2.1 Participants:
The participants were female (n=20) registered students from two different universities in Table
Tennis training lessons. All the students were female and were those who knows a little bit
about table tennis but all the subjects were considered in beginning phase in learning table
tennis. Those subjects who ever held table tennis bat were not excluded from the investigation
after making sure that they did not know how to play properly. The participants were separated
into two groups: an experimental (N = 5/5) and a Control (N = 5/5). The Experimental Group
(E) used shadow training in combination with multiple-ball practice; and the Control Group (C)
practiced with one ball per pair of athletes in combination with multiple-ball practice.
2.2 Tool:
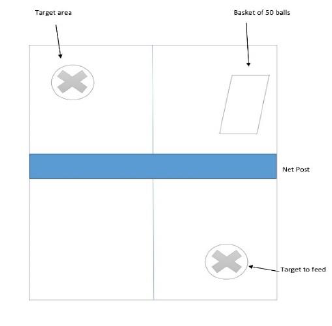
The consistency and accuracy ability test were utilized to decide the scores of the participants.
An overall of 100 mentor balls were utilized for the test and two people, the feeder and the
counter managed the test. The test was directed with each subject in turn. Each subject was
taught to hit the same number of balls as she can to the assigned goal territory (crosscourt) at the
contrary court. The total of balls that hit the predetermined objective territory was checked (e.g.,
50/50, 50/100). The consistency and accuracy of the participants in accomplishing the forehand
and backhand-drive were established throughout the pre, post and retention trails.
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4493
The standard forehand drive was chosen as the trial task. Since this exposed skill is essential to
the sport of table tennis. It is additionally ordinarily first in the learning order in every table
tennis lessons after the introductory of the essential mechanics, as the hold grip style and the
fundamental prepared position. As per for backhand, the assignment was to implement the
standard backhand-drive. The guidelines were as per the following: Preparatory stage: arm ought
to be loose; the racket point ought to be roughly 90º and the wrist ought to be free. Execution
stage: bring racket directly toward the abdomen at that point broaden elbow forward; contact
ought to be made forward-facing the body, at that point finish (Hodges, 1993). All participants
were additionally encouraged to, "consistently contact the ball as low to the table as could
reasonably be expected, in 6 inches of it. That way, it won't bob as high on the far-off side. It
will likewise make it simpler to serve short" (Hodges, 1993).
Following the underlying preparation, the participants were given the Pre-test to build up the
standard data. The subjects were randomly consigned to training conditions after the pre-testing
stage, the Experimental Group utilized shadow practice, in mix with multi-ball practice while the
Control Group rehearsed by performing one ball practice in mix with multi-ball practice.
In the training lessons, every one of the subjects practice multi-ball drills, wherein the ball feeder
throws separate balls for each stroke as opposed to utilizing just one ball (Letts, 2008).
The participants of the Control Group were taught to strike the ball (diagonally) and attempt to
keep their development in a "controlled" way and were not permitted to crush the ball even
though achieving control on ball with their strokes throughout the ten-day treatment period. The
Experimental Group was requested by the trainer to execute shadow practice and were allocated
ten minutes to constantly play out the activity (Florendo Fernando, 2007)(Florendo, The
Effectiveness of Shadow Practice in Learning the Table Tennis Backhand Drive, 2010). The
initially set was done before the multiple-ball practice lesson and the second arrangement of
shadow practice was done later.
The Training period was for 4 weeks alternate days for each group, following the ten-day
treatment period for each group, the subjects were exposed to a Post-test. They followed a
similar technique as the Pre-test.
After the post-test, the participants were prearranged a four-day rest period at that point was
given the Retention-test that followed the methodology completed during the pre as well as post-

ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4494
tests. The total of balls to hit the predefined target region will be the Participant's Retention-test
score.
2.3 Data Analysis:
Data was evaluated by utilizing the t-test to define major changes in the two classes' pre-test,
post-test and retention-test. Independent sample was utilized to define notable distinction
between the two participant classes' post-tests as well as retention-test. Though, paired-sampling
was utilized to determine the pre as well as post-test, just as (PT) and (RT) between both
participant groups. The degree of significance was adjusted at p = 0.05.
STATISTICAL RESULTS
Table 1 represents a huge distinction in the mean scores concerning the pre-trail and post-trial of
the focus group. The pre-trail scores of FSP experimental class were 18.80 ± 1.92 and the post-
trail scores 39.20 ± 1.304. But the RT scores 39.40 ± 1.140 it likewise represents that there is no
major variation among the mean scores in their post-trail and RT. The result proposes that the
valuable impact of utilizing shadow practice isn't impermanent in type however can conclusively
influence the learning of standard forehand counter-drive. Shadow training empowered the
subjects to have a figure of co-ordination and gave them a knowledge with regards to what the
"objective development design of striking the ball feel" (Gavan Lintern, 1978). They had what
(Schmidt, 1991) and (Craig A. Wrisberg, 1991) expressed as their own "proprioceptive or
physical data". They may have intentionally or unknowingly encountered the development of
their joints and along these lines build up their muscle memory that in the long run got
programmed as they shadow training (Packer, 2005). The discoveries additionally demonstrated
that the players can utilize the experience of shadow training to abbreviate the learning
procedure, which is to arrive at a more developed level execution in less time.
Table 1. Mean and standard deviation of Forehand Experimental Group's scores
Mean Scores
Standard
Deviation
T(N-5)
Sig(2-tailed)
Pre-Test
18.80
1.924
--
--
After one week
22.20
0.837
-4.543
0.010
2nd week
25.40
2.191
-2.997
0.040
3rd week
30.60
1.673
-3.833
0.019
4th week
34.20
3.033
-2.207
0.092
Post-Test
39.20
1.304
-3.162
0.034
Retention-Test
39.40
1.140
-0.250
0.815
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4495
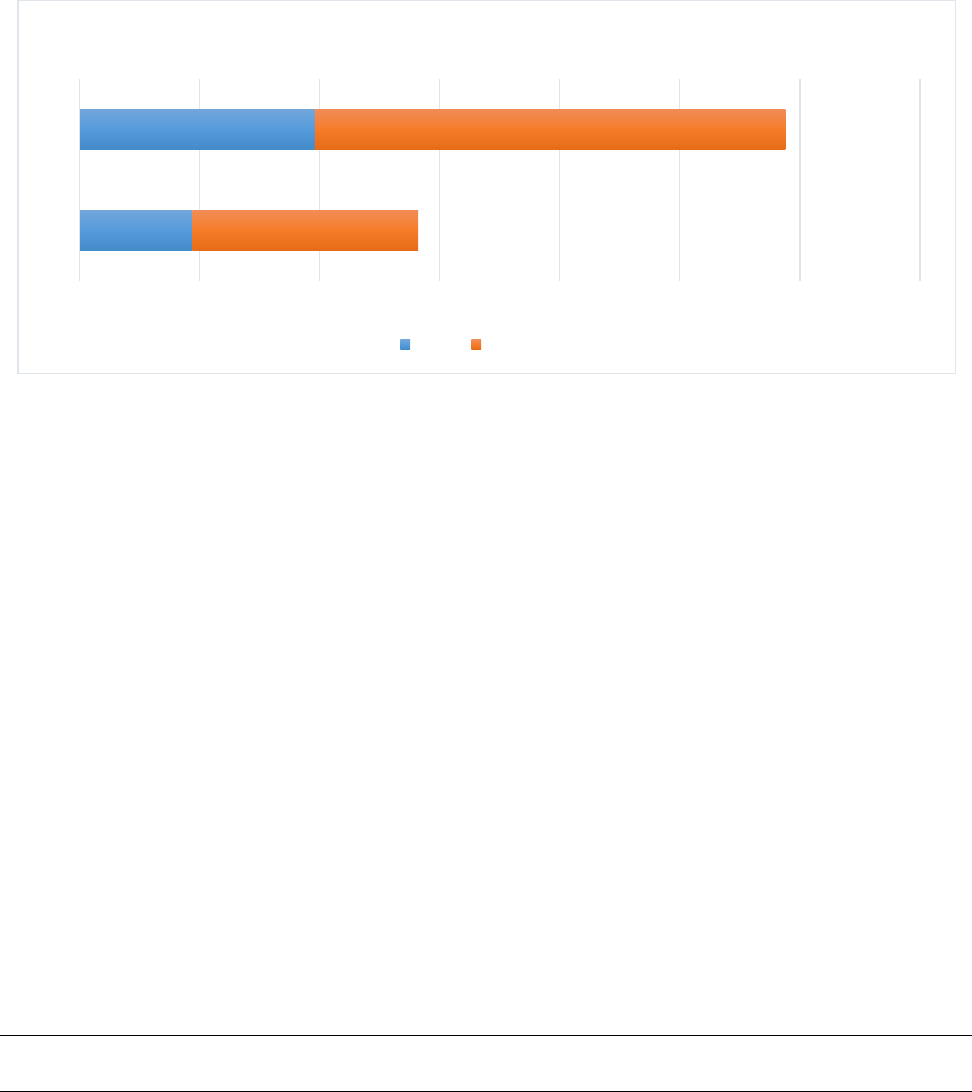
Figure 1. Forehand Shadow Practice (EG)
Figure 1 is representing pre-trail as well post-trail per-formance of forehand ex-perimental group
that as in pre-trail per-formance 37.6 % and after training performance has improved to 78.4 %.
Table 2 indicate a huge contrast between the mean scores of the pre-trail also post-trial of the
comparison group. The pre-trail scores of FSB control class was 18.60 ± 2.302 and the post-trail
scores 38.00 ± 1.581. But the RT scores 35.80 ± 1.304 it likewise represents a huge contrast
between the mean scores of their PT and RT scores as the scores remained lower in RT. The
comparison group played with a one ball as they trusted that their turn will rehearse with multi-
balls. They were told to play the ball crosscourt or corner to corner with a controlled activity.
They halted to get the ball more regularly than attempting to keep it on the table. As previous
researches that have discovered that skillfulness learning is emphatically identified with effective
practice preliminaries and adversely identified with fruitless practice (Ashy, 1998); (Edward P
Hebert, 1996) halting to collect balls missed decreased the duration of actual training period.
They couldn't encounter the objective development example of striking the ball cross-table since
they had additional time getting the ball than placing it in play. The discoveries negated what
could be predictable from a direction theory perspective (Schmidt, 1991) that creating the
training knowledge more troublesome outcomes in the weakening of securing performance
however improves RT. The comparison group remained to accomplish high scores as appeared
in their post-test yet couldn't hold their scores as appeared in their RT.
Table 2. Mean and standard deviation of Forehand Control Group's scores
Mean Scores
Standard
Deviation
T (N-5)
Sig(2-tailed)
Pre-Test
18.60
2.302
---
---
After one week
21.40
1.140
-2.123
.101
2nd week
25.80
2.280
-3.641
.022
3rd week
30.00
1.581
-2.537
.064
18.8
39.2
37.6
78.4
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
pre
post
Forehand Experiment Group Performnace Chart
FHEG performance
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4496
4th week
33.60
2.510
-2.025
.113
Post-Test
38.00
1.581
-4.274
.013
Retention-Test
35.80
1.304
2.750
.051
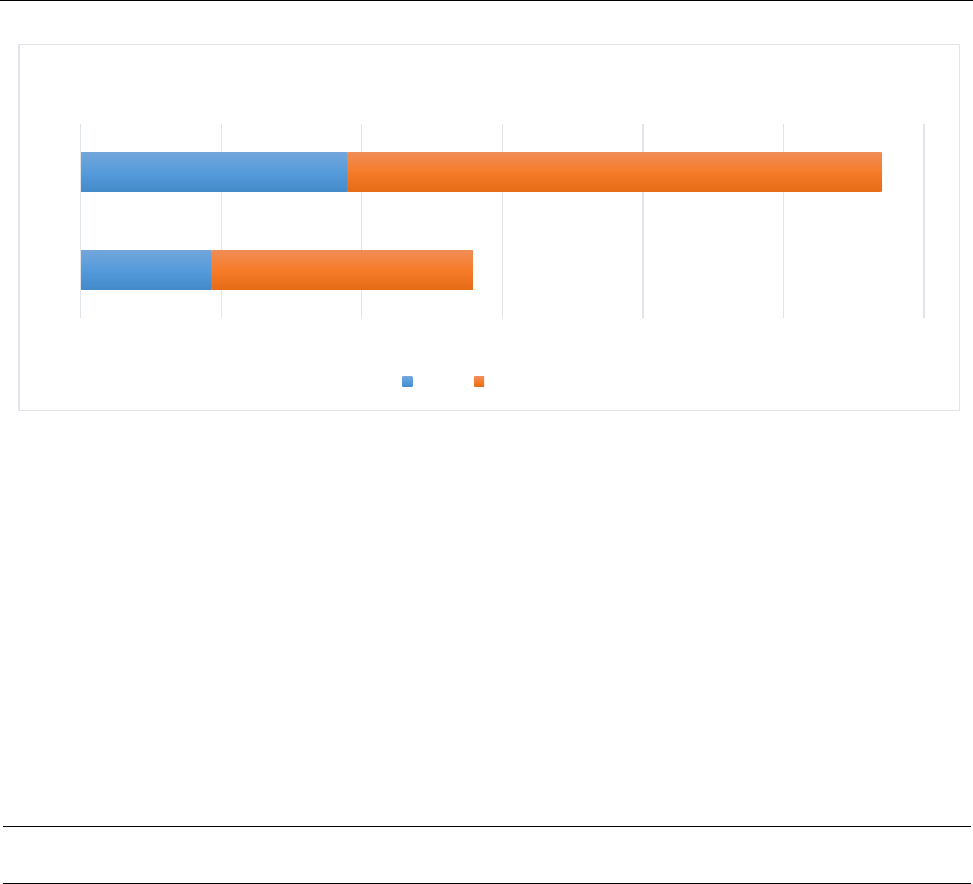
Figure 2 Forehand Single Ball (CG)
Figure 2 is representing pre-trail as well post-trail per-formance of forehand Control group that
as in pre-trail per-formance 37.2 % and after training performance has improved to 76 %.
Table 3 represent the mean scores of both the pre-trail and post-trial of the Ex-perimental Group
which were altogether significant. The pre-trail scores of BSP ex-perimental class was 18.60 ±
1.140 and the post-trail scores 39.60 ± 1.140. But the RT scores 39.80 ± 1.643. It indicates there
is no huge contrast bet-ween the mean scores in the PT and RT. The discoveries propose that the
helpful impacts of utilizing shadow practice are not transitory in nature but rather can
emphatically influence the learning of the standard backhand counter-drive.
Table 3. Mean and standard deviation of Backhand Experimental Group's scores
Mean Scores
Standard
Deviation
T (N-5)
Sig(2-tailed)
Pre-Test
18.60
1.140
---
---
After one week
22.00
1.225
-4.185
.014
2nd week
20.60
1.342
-9.021
.001
3rd week
31.00
1.000
-6.487
.003
4th week
34.60
2.793
-3.674
.021
18.6
38
37.2
76
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
pre
post
Forehand Control Group Performance Chart
FHCG performance
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4497
Post-Test
39.60
1.140
-3.162
.034
Retention-Test
39.80
1.643
-.535
.621
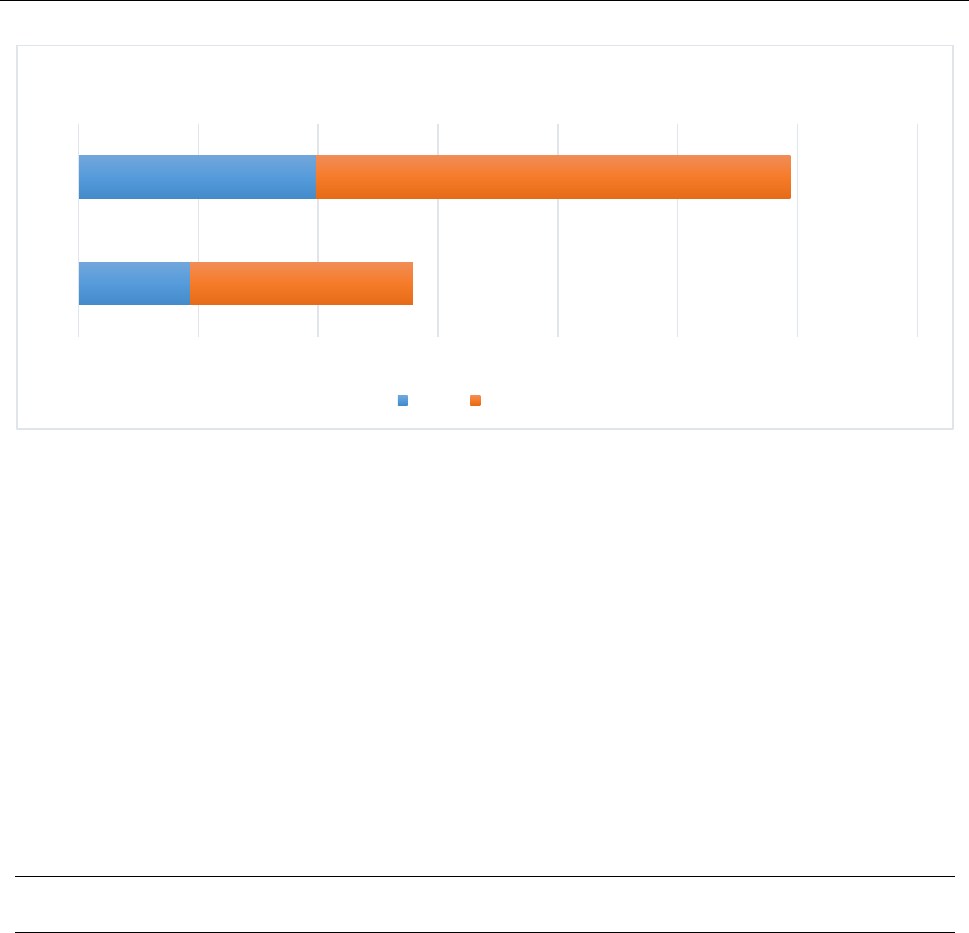
Figure 3 Backhand Shadow Practice (EG)
Figure 3 is representing pre-trail as well post-trail performance of backhand experimental group
that as in pre-trail performance 37.2 % and after training performance has improved to 79.2 %.
Table 4 represent the mean scores of the pre-trail and post-trial of the Comparison Group. The
pre-trail scores of FSP experimental class were 18.40 ± 2.074 and the post-trail scores 38.00 ±
1.581. But the RT scores 36.20 ± 1.304. The CG played with a solitary ball as they trusted that
their turn will rehearse with multi-balls. They were able to increase the performance regardless
of whether they invested a portion of the energy getting the ball as opposed to keeping it in
practice. The multiple ball training session incredibly helped them in building up a specific
degree of automaticity since it included reliable improvement reaction planning "where the
upgrade design consistently requires a similar reaction" (Richard A. Schmidt, 2004). TheCG was
additionally ready to accomplish high scores in their post-test.
Table 3. Mean and standard deviation of Backhand Experimental Group's scores
Mean Scores
Standard
Deviation
T(N-5)
Sig(2-tailed)
Pre-Test
18.40
2.074
---
---
After one week
21.00
1.000
-5.099
.007
2nd week
26.00
.707
-9.129
.001
3rd week
29.40
1.140
-5.013
.007
4th week
33.80
1.304
-5.047
.007
Post-Test
38.00
1.581
-11.225
.000
18.6
39.6
37.2
79.2
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
pre
post
Backhand Experiment Group Performance Chart
BHEG Performance
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4498
Retention-Test
36.20
1.304
1.857
.137
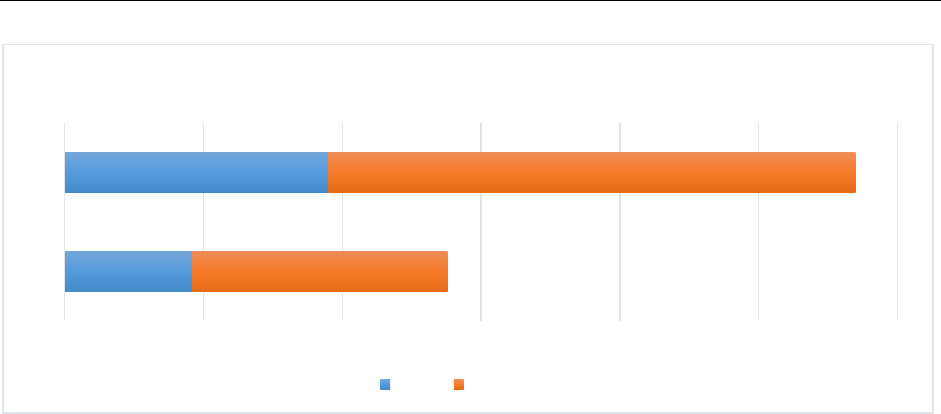
Figure 4 Backhand Single Ball (CG)
Figure 4 is representing pre-trail as well post-trail performance of backhand control gathering
that as in pre-trail performance 36.8 % and after training performance has improved to 76 %.
DISCUSSION
The discoveries that review on response have given supported its being summed up to applied
circumstances. Though, larger part of these investigations had been directed in sports center
settings which may have some dissimilarity when contrasted with research settings. Hebert,
Landin and Solomon (1996) expressed that "contrasted with common research center
responsibility, athletic abilities are commonly more unpredictable developments, include the
dominant of a largernumber of degrees of self-determination, and necessitate more training to
dominant"(pg. fifty-three). In accordance with (Amelia M. Lee, 1993) proposal that "those
attestations be established in Table Tennis practice halls" (pp. 228 – 243), this investigation was
directed to watch the exhibition of Table Tennis beginner university level players utilizing the
direction method of (SP) in mastering the (TT) standardized forehand and backhand drive.
Mostly university in Pakistan lack of (TT) tables to mark the perfect unit of athletes however is a
two-practice partner for one table. Table Tennis Coaches or P.E. educators experience trouble
encouraging learning in circumstances where there are a greater number of players than what
could really be obliged and with a constrained time. The study has a normal of twenty
participants registered at their one hour for both group (experimental and control) table tennis
training session. Though, the study prepared three tables for training. One university has three
table and the other one has one table in their practice hall. Regardless of whether the universities
could bear to buy extra tables, there would in any case be difficulties on how these tables would
be used. The training session is led simultaneously with table tennis coaches; in this manner they
just have a distributed space in the university sports hall. How learning can be more helpful in
these universities and in different universities with comparable circumstances is likewise the
18.4
38
36.8
76
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
pre
post
Backhand Control Group Performance Chart
BHCG performance
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4499
distress why this examination planned to check whether shadow practice is a viable mode for
techniques guidance.
An overall of 20 females from two different university volunteer players by a mean 18 years old
were considered as participants for this examination. In this investigation five participants got the
training of forehand-drive shadow practice with combination of multi-ball, and five participants
got the training of (FD) a single ball practice per pair with combination of multi-ball. Similar
with backhand drive five participants got the backhand shadow practice with a combination of
multi-ball and five participants got the (BD) a single ball training per pair with combination of
multi-ball. The experimental group includes the five students of forehand drive and five students
of backhand drive who got the shadow practice with combination of multi-ball training. Same
method as control group includes the five students of forehand and five student of backhand
drive who got the single ball per pair training with mix of multi-ball. All were viewed as
unadulterated novice in the game of table tennis. The individuals who at any point held a table
tennis racket but never took any table tennis lesson or play at even in minor competition
considered in this study but 60 % students in the study were beginner who never held table tennis
racket. Those volunteered who ever play any competition or know any skill of table tennis were
dejected from offering their participation in during the spread of the examination to the
distinctive table tennis training lesson. The subjects were pre-test FSP gatherings' mean = 18.80;
FSB control gathering's mean = 18.60 and BSB gathering’s mean = 18.60; BSB gatherings’
mean = 18.40 haphazardly allocated to both of experimental as well as control participant
gatherings. They’re approached to present physically for 1 month for their training after that a
post (FSP test gathering's mean = 39.20; FSB control gathering's mean = 38.00 also BSP test
gatherings’ mean = 39.60; BSB control gatherings’ mean = 38.00 was managed following 3
schedule days from the post-testing stage. Information was investigated utilizing descriptive
measures, t-test (FEG) t = -3.162, post and (BCG) t = -3.162, maintenance test (FEG) t = -250;
and (BCG) retention t = -.535; (FCG) pre and post-test t= -4.274, and (BCG) t = -11.225; and
Retention Scores (FCG) t = 2.750; and (BCG) t = 1.857).This investigation uncovered that two
of the treatment class and comparison class ensured a substantial difference in scores in their
post-trial period of analysis. In any case, just the treatment class had the option to hold different
score in the (RT) period of analysis.
In this investigation, the two gatherings were competent to perform the forehand and backhand
drive successfully as initial of schedule by way of the pre-trail when contrasted with (Florendo
Fernando, 2007). Their [Florendo and Bercades] mean scores on the Forehand Drive Pre-test for
the Comparison class were 37.3 ± 14.99 and for the treatment class was 36.8 ± 16.37 while this
investigation shows a mean score of 67.2 ± 17.8 for the treatment Class and 64.57 ± 20.59 for the
Comparison class.
Indeed, level with the aspect of a cord which have been utilized in the previous research
completed by (Florendo, The Effectiveness of Shadow Practice in Learning the Table Tennis
Backhand Drive, 2011), the participants despite everything got higher scores when contrasted
with examination done by (Florendo Fernando, 2007) which didn't utilize a string, so the same
procedure for without string has been used in this current investigation. The correlation of the
outcomes indicates that drive from backhand side is easier to perform than the forehand ( (Navy,
1999) as prove by their greater scores acquired by the two gatherings (Control group and
Experimental group) in the current examination. Though the outcomes show that experimental
class that forehand and backhand drive scored higher than the control group with the single ball
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4500
per pair training. The experimental group got the higher scored in their (RT) and show the
positive and difference comparing with the control group. But with the comparison between
experimental group (Forehand and Backhand drive) appeared that the drive from backhand side
is a lot easy to execute as compared to the forehand. Because the forehand drive-spin is much
difficult to execute because it includes different arm swing, footwork, body rotation, and weight
transfer but as compare to drive from backhand side it does not include footwork, physical
turning, and transfer of weight. In this investigation, there weren’t any huge contrasts (p > 0.05)
from their (PT) to the (RT) for the two gatherings (Experimental Group and Control Group) that
implies the two gatherings had the option to hold their scores. Though this implies for the
examination, both shadow training and Solitary-ball training joined with multiple-ball training
could assist starting with leveling players become familiar with the reliable and exact forehand
and backhand drive. However, the useful impacts of utilizing shadow training is not short-term in
type but rather could emphatically influence the mastering of table tennis skills.
CONCLUSION
The discoveries of the investigation assist the researches (Wulf G. S., 1998); (Wulf G. S., 1998)
and (Florendo and Bercades (2007) (2011) which had likenesses in the outcomes. Precisely, the
outcomes repudiated what can be anticipated from a Guidance theory perspective (Schmidt,
1991). Though outcomes of this investigation prompted the end that two of the training shadow
training along with utilizing a one ball for two player pair each prompted higher scores in the
(PT). Arithmetically managed information uncovered that solitary the individuals who completed
shadow training had the option to hold theirs scores in the (RT) while the individuals who
rehearsed with one ball for each pair ensured an essentially lesser score in their (RT) when
contrasted with their (PT). Hence, this investigation uncovered that utilizing shadow training is
beneficial method for viable ability guidance. The examination presumed that there isn’t any
critical contrast between the two-participant gathering's Pre-and Post-trail. The two gatherings
remained to accomplish higher scores in their PT.
The treatment class utilizing shadow training didn't display any noteworthy distinction in the
post-test plus (RT). Hence, this gathering was capable toward maintaining the scores in (RT).
Though, there was a critical difference between comparison class’s post-T and RT scores. The
comparison class utilizing one ball for each pair couldn't hold their scores in the maintenance
test.
RECOMMENDATION
For additional examinations regarding the matter, it is suggested that the cord can be use with
table net post addition to be height of 6 inches (initially fourteen inches) to get an advanced
quality. It is additionally prompted that the investigation would concludes better result if it done
with an equivalent number of members by 32.
It ought to be suggested that upcoming examinations include male participants as what (Craig A.
Wrisberg, 1991) did in expanding the teaching of 3 badminton serves (pg. 406-12). Their
examination included male participants since (Sinah Goode, 1986) investigation had just girls as
participants (pg. 308-14). Their discoveries indicated that there wasn’t divergence among both
counterpart (the male and the female participant's) performance. Additional investigations permit
to likewise check whether it could determine similar outcomes.
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4501
Lastly, since the two gatherings performed multiple-ball training, a similar report concerning
multiple-ball and shadow training ought to likewise be completed in future examinations to
understand that which one would be a more successful practice technique.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The Research was conducted in Kinnaird College for Women. First of all, I would like to thank
to Allah who enabled me to accomplish this research. I would like to thank and express my
sincere gratitude, appreciation to my lovely parents who have been providing all of their support
by simply being there for me throughout.
REFERENCES
Amelia M. Lee, N. K. (1993). Instructional Effects of Teacher Feedback in Physical Education.
Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 228-243.
Ashy, M. L. (1998). Relationship of practice using correct technique to achievement in motor
skil. Journal of Teaching Physical Education , 115 - 120.
Craig A. Wrisberg, Z. L. (1991). The effect of contextual variety on the practice, retention, and
transfer of an applied motor skill. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 406-412.
Edward P Hebert, D. L. (1996). Practice Schedule Effects on the Performance and Learning of
Low- and High-Skilled Students: An Applied Study. Research quarterly for exercise and
sport, 52-58.
Elzbieta Biernat, S. B. (2018). Eye on the Ball: Table Tennis as a Pro-Health Form of Leisure-
Time Physical Activity. International journel of Enviromental Research and public
Health, 1-11.
Florendo Fernando, B. D. (2007). THE EFFECTIVENESS OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN
LEARNING THE TABLE TENNIS STANDARD FOREHAND DRIVE. 10th
International Table Tennis Sports Sciences Congress, (pp. 1-8).
Florendo, F. (2010). The Effectiveness of Shadow Practice in Learning the Table Tennis
Backhand Drive. International Journal Of Table Tennis Sciences , 105-110.
Florendo, F. (2011). The Effectiveness of Shadow Practice in Learning the Table Tennis
Backhand Drive. International Journel of Table Tennis Sciences, 105-110.
Gavan Lintern, D. G. (1978). Adaptive training of perceptual-motor skills: issues, results, and
future directions. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 521-551.
Hodges, L. (1993). Table Tennis: setps to success. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics Publishers.
Jacqueline M. Edwards, D. E. (1986). Contextual Interference Effects during Skill Acquisition
and Transfer in Down’s Syndrome Adolescents. Research in Adapted Physical Activity
Quarterly, 250-258.
John B Shea, R. L. (1979). Contextual interference effects on the acquisition, retention, and
transfer of a motor skill. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Learning and
Memory, 179-187.
ANALYSIS OF TABLE TENNIS SKILLS: AN ASSESSMENT OF SHADOW PRACTICE IN LEARNING
FOREHAND AND BACKHAND DRIVE PJAEE, 18(8) (2021)
4502
Letts, G. (2008, May). Table Tennis/Ping Pong Training-Using Multiball in Your Ping Pong
Practice. Retrieved from http://tabletennis.about.com/od/trainin1/a/multiball.htm
Mehmet Fatih YÜKSEL, L. A. (2017). The Effect of Shadow Badminton Trainings on Some the
Motoric Features of Badminton Players. Journal of Athletic Performance and Nutrition,
4(2), 11-28.
Navy, R. (1999). Table Tennis, Retrieved May 2008. The Royal Marine.
Olivier Girard, G. P. (2009). Physical Determinants of Tennis Performance in Competitive
Teenage Players. The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 1867-1872.
Packer, S. (2005). Department of Cellular and Integrative Physiology. Indiana University.
Richard A. Schmidt, C. A. (2004). Motor Learnig and Performance. Champaign, United States:
Human Kinetics Publishers.
Schmidt, R. (1991). Frequent augmented feedback can degrade learning. Evidence and
Interpretations. In J. Requin & G. E. Stelmach (Eds.), NATO ASI series; Series D:
Behavioral and social sciences,, 59-75.
Sinah Goode, R. A. (1986). Contextual Interference Effects in Learning Three Badminton
Serves. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 308-314.
Wei Zheng, K. j. (2016). Multi ball training method: a new attempt of table tennistraining in
college and university. 5th international conference on social science,education and
humanities research , 1-4.
Wulf, G. S. (1998). Frequent feedback enhances complex motor skill learning. Journal of Motor
Behavior, 180-192.
Wulf, G. S. (1998). Physical guidance benefits in learning of complex motor skill. Journal of
Motor Behavior, 367-380.
Yaodong Gu, C. Y. (2019). Effects of table tennis multi-ball training on dynamic posture control.
Peer J.
